Key Takeaways
- Industrial dewatering is essential for efficiency but introduces specific safety challenges.
- Adherence to regulatory standards such as OSHA is non-negotiable for risk management.
- Regular equipment maintenance, comprehensive training, and appropriate PPE are critical in safe operations.
- Technological advancements are reshaping how safety and efficiency are achieved in dewatering applications.
Introduction
Industrial dewatering stands as a cornerstone process within sectors such as mining, construction, and wastewater treatment. It ensures that operations remain safe, efficient, and free of the disruptions water accumulation can cause. However, the complex nature of handling water and heavy-duty equipment introduces unique safety challenges that organizations must proactively address to safeguard their workforce and assets. Solutions such as mechanical dewatering are vital for maintaining site stability, especially in environments where seasonal floods or ground saturation can threaten progress and worker safety.
Building a culture of safety in industrial dewatering operations requires companies to prioritize regulatory compliance, worker training, and continuous innovation. Early recognition of hazards, the use of specialized equipment, and worker vigilance are foundational pillars for a safe working environment and improved productivity.
READ ALSO: How Media Blasting Enhances Surface Preparation Across Industries
Understanding Dewatering and Its Applications
Dewatering refers to the systematic removal of water from solid material or soil. This essential process can be accomplished using various mechanical techniques—including pumps, hydrocyclones, drying beds, or filtration units—to eliminate excess water that may obstruct construction digs, mining tunnels, or industrial work zones. As seen in large-scale mining projects across regions like the Democratic Republic of Congo, failing to dewater adequately can halt production, cause equipment failures, and pose health and safety risks to onsite personnel.
Robust dewatering systems do more than expedite operations—they are crucial in environmental management and regulatory compliance, restricting surface runoff and minimizing the spread of contaminants. For instance, wastewater treatment plants depend on dewatering to optimize the disposal of biosolids, while construction sites use it to stabilize soil and foundation works.
Common Safety Hazards in Dewatering Operations
Despite its utility, dewatering can pose several safety risks that organizations should address to prevent accidents and operational disruptions:
- Equipment Malfunctions: Pumps and hoses subject to frequent use or improper maintenance can fail unexpectedly, endangering workers nearby.
- Electrical Hazards: Water and electrical systems must be rigorously separated and managed. Exposed wiring or submerged electrical panels can result in electrocution or burns.
- Confined Spaces: Dewatering often occurs in trenches, tanks, and pits, creating the potential for asphyxiation, toxic exposure, or physical entrapment.
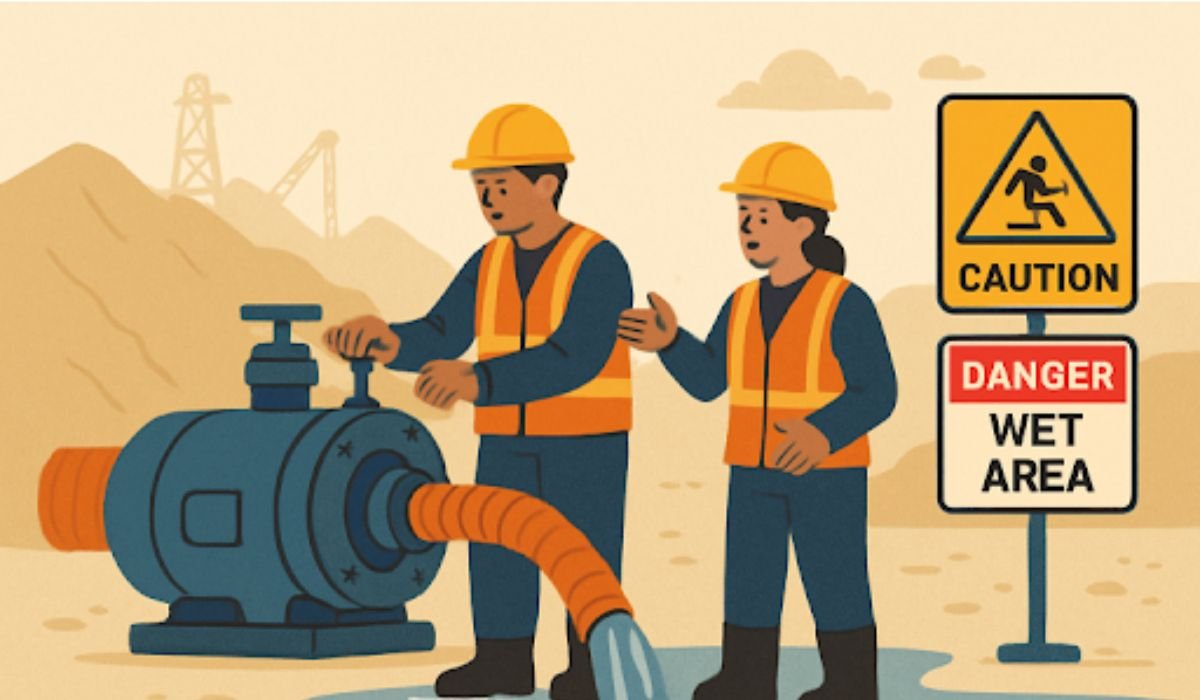
- Slip and Fall Incidents: Wet and cluttered surfaces are common on dewatering sites and can lead to serious falls and injuries.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Compliance with regulatory standards is essential for mitigating workplace risks in dewatering operations. Government agencies such as the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have issued detailed regulations for managing confined spaces, fall hazards, and electrical safety. Violations can lead to severe injuries, legal consequences, and reputational damage.
Companies must develop, implement, and enforce safety programs that meet and exceed minimum compliance standards. Lessons from documented incidents—such as companies being fined for lack of fall protection or improper confined space protocols—underscore the consequences of neglecting safety and the importance of a robust safety management program.
Implementing Effective Safety Measures
Addressing dewatering hazards requires a multi-faceted safety strategy:
- Regular Equipment Maintenance: Routine inspections and scheduled servicing ensure machinery and components function safely and effectively. Preventive maintenance avoids breakdowns and reduces unplanned downtime.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Regular training equips workers with up-to-date guidance on emergency procedures, equipment handling, and the specific hazards associated with dewatering activities.
- Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Every site should ensure workers are equipped with suitable PPE—such as waterproof boots, safety helmets, gloves, and visibility vests—to minimize direct exposure to risk factors.
- Clear Signage and Barriers: Effective site management includes physical barriers and clear warning signs around hazardous zones, minimizing the likelihood of unauthorized entry or accidental contact with unsafe areas.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Safety
Technological advances are transforming the safety landscape of industrial dewatering. Real-time remote monitoring systems can detect pump inefficiencies or imminent failures, enabling rapid intervention before hazards escalate. Automated alert systems now provide early warnings about hazardous working conditions, while filtration and separation innovations reduce contaminant risks and environmental impact.
Furthermore, digital platforms for managing worker certification, maintenance schedules, and compliance records streamline oversight and enable swift action on emerging threats, placing organizations at the forefront of proactive safety management.
Final Thoughts
Any organization aiming for long-term operational excellence must prioritize the safety of industrial dewatering operations. By marrying traditional risk management strategies—such as diligent maintenance and good training—with new technologies and strict compliance, organizations can dramatically reduce the frequency and severity of workplace incidents. Commitment to continuous improvement and proactive adaptation is the blueprint for keeping every worker safe while meeting productivity goals.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: SOA OS23: Your Key to Demolition Contracts